If you or someone you care about is up for a pacemaker surgery, it is quite natural to have questions about the process. One of the most frequently asked questions is the timeline; “How long does the pacemaker implantation surgery actually take?” We are here with your answer.
How Long Does Pacemaker Implantation Take?
The procedure of implantation is relatively uncomplicated. It is typically performed under the effect of local anesthesia; this means that you will remain conscious throughout the procedure but won’t feel a thing.
If we talk about the average timeline, a pacemaker surgery takes no longer than an hour. However, if you are opting for a biventricular pacemaker that comes with three leads or have to combine a regular one with other heart surgeries, the duration might extend. Other than that, if you add a recovery period after implantation, you will most likely spend the night in the hospital and take a day of rest to ensure a smooth recovery.
Preparing for Pacemaker Surgery
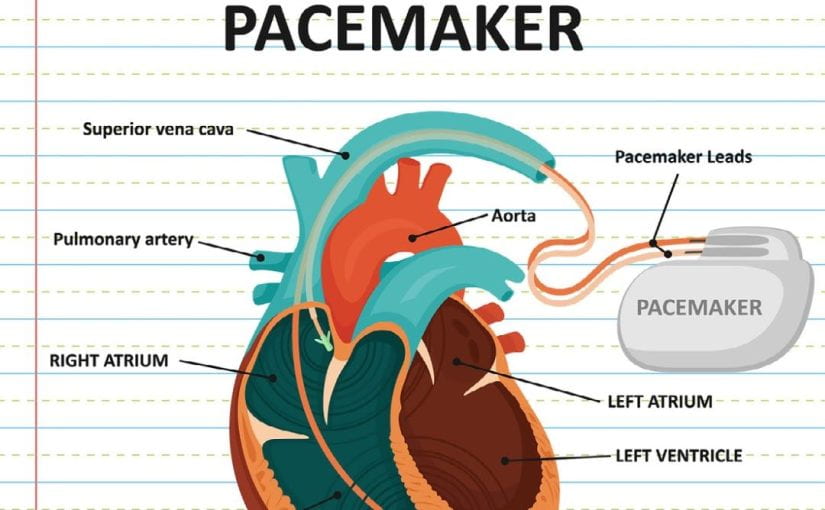
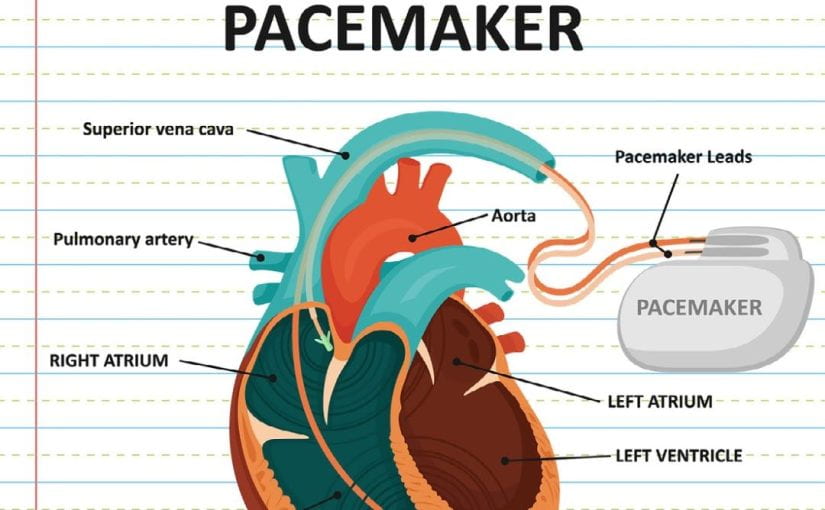
A pacemaker device is a small battery-operated gadget that is placed under the skin in the muscle near your collarbone. It is then connected to a wire, carefully passing over a blood vessel to reach your heart.
Expect a preoperative assessment before the actual surgery. During this, your cardiologist will thoroughly check to ensure your fitness for the procedure. In this meeting, you can freely discuss anything about the operation and clarify lingering questions. Various tests, such as blood tests and an electrocardiogram (ECG), are conducted to jot down crucial information about your health and heart condition.
Types of Pacemaker Surgeries
- Catheter-Based Approach: When the cardiologists select leadless pacemakers for single-chamber heart conditions, they insert a catheter into an artery. The placement needs an entrance near the groin, threading it up to the heart and attaching it to the heart’s wall.
- Transvenous (Through a Vein): This method is commonly used in adults. It involves making a small incision to access a vein near the heart, which is usually found beneath the collarbone. With the help of fluoroscopy, a type of X-ray, they thread wires through the vein, attaching them to a point in the heart. Then, the device is placed under the skin of the upper chest.
- Surgical-Based: As the name suggests, surgical intervention means a small chest incision through which the leads go through and attach to the heart. The pacemaker is then placed in a pocket-type space under the skin of the abdominal area. Catheter-based procedures can take as long as an hour or even less; on the other hand, transvenous and surgical-based approaches may take between 2-5 hours.
Life Expectancy with a Pacemaker
The life expectancy of anyone with a pacemaker inside is dependent on various factors, primarily age and existing health conditions. If you have fewer or fewer health concerns, expect to enjoy a longer and more normal life expectancy after pacemaker implantation.
Closing Note
Learning about the process of pacemaker implantation can help you understand more about the duration of this surgery. At Atrial Fibrillation Centers of America, Dr. Shanti Bansal – board certified in Internal Medicine (2010), Nuclear Cardiology (2011), and Electrophysiology (2013), and the team makes sure to deal with all aspects of your cardio needs. You can consult us at (832) 478-5067 or give us a visit in Houston, TX, for more questions or queries.